The previous section mentioned that a suitable toughening agent must be selected for nylon toughening. In this section, we share another important factor – how to understand and choose nylon.
Among the modified nylon, usually more than 90% are nylon 6 and nylon 66, that is, PA6 and PA66, which account for more than 90% of the entire nylon modification.
Therefore, in this section, I will tell you how to understand and choose nylon 6 and nylon 66.
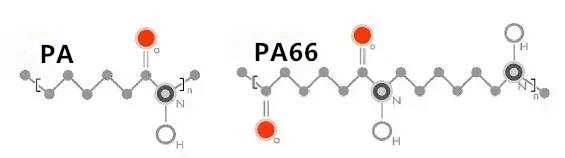
(Nylon 6 and Nylon 66 molecular formula)
For PA6, it can usually be divided into three categories. From the perspective of viscosity, it can be divided into high viscosity, medium viscosity and low viscosity.
1.High viscosity nylon
Viscosity above 3.0
Generally speaking, high-viscosity nylon, because of its high viscosity, has better comprehensive physical properties, stretch bending and punching. It is used as a composite material toughened by nylon, and its comprehensive properties are better.
2.Low viscosity nylon
Low viscosity refers to below 2.4
Skip the medium viscosity and directly talk about low viscosity. Because of low viscosity, low viscosity brings good fluidity. When doing nylon toughening, it can make the toughening agent form a relatively large particle size distribution, thus reflecting the normal temperature impact It is also relatively good, but due to its viscosity problem, the low temperature resistance performance is reduced.
3.Medium viscose nylon
Viscosity 2.7-2.8
The most commonly used is of course medium-viscosity nylon, but people often find that when medium-viscose nylon is used for toughening, the impact strength at room temperature is often not easy to improve. In this case, it is recommended to compound a small amount of low-viscosity nylon on the basis of using medium-viscosity nylon, so as to increase the impact strength at room temperature while ensuring low-temperature performance, so as to ensure fluidity and reflect the properties of nylon toughened materials. Effect.











