Most nylon for high temperatures is semi-aromatic. Due to its excellent heat resistance, minimal water absorption, and good dimensional stability, it is frequently used in industries with specialized needs including the aerospace, automotive, and electronic appliance industries. There aren’t many research studies available right now on the toughening agent for high-temperature nylon composites bonded with glass fiber. Based on this, the mass fraction of glass fiber is set at 20%, and POE-g-MAH toughened PA66 and high-temperature nylon materials are studied for their effects on the mechanical properties of high-temperature nylon composite materials and potential mechanisms for improving high-temperature nylon materials with glass fiber reinforcement.

Adding only POE-g-MAH compared to its toughened high temperature nylon and PA66
1. Comparison of mechanical performance data
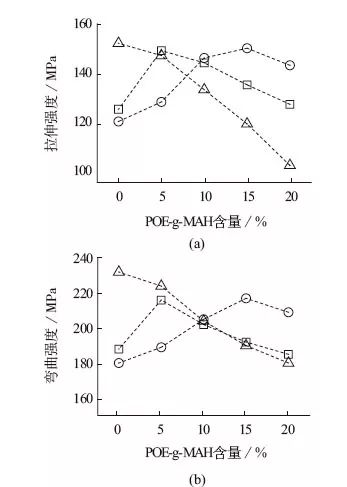
The tensile strength and flexural strength both decreased in the PA66 system as POE-g-MAH content increased, whereas in the PA6T/66 and PA10T systems, they both increased before decreasing. It was also discovered that there is a significant difference in the amount of POE-g-MAH added when the strength of the two reaches its maximum. When the PA6T/66 system achieves its maximum strength, around 5% of POE-g-MAH is added, and when the PA10T system reaches its maximum strength, 10%. About 15% of POE-g-MAH has been added.
2. The mechanism seen from the scanning electron microscope pictures
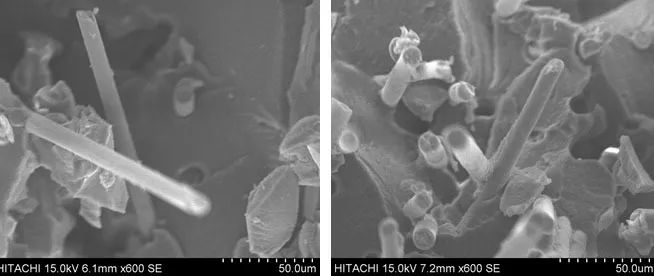
The content is 0 and the content is 5%
20% glass fiber reinforced PA6T/66 with different POE-g-MAH content

20% glass fiber reinforced PA66 without POE-g-MAH
In the high-temperature nylon system without adding POE-g-MAH, the bonding between the glass fiber and the resin is poor, as can be seen from the above figure where the glass fiber surface on the impact spline section is very smooth and there is no obvious sign of nylon matrix coating. On the spline section of the PA6T/66 system with 5% POE-g-MAH added, it is discovered that the surface of the glass fiber has obvious wrinkles, indentations, The matrix resin effectively functions as an interfacial compatibilizer by covering POE-g-MAH.
As seen in the image below, the glass fiber and resin work well together in the PA66 system without POE-g-MAH, and the glass fiber is plainly covered with nylon resin.
On the basis of this, we assume that the higher processing temperature of high-temperature nylon results in the degrading loss of the intrinsic coupling agent on the surface of the glass fiber and poor bonding between the glass fiber and the resin. In the system with POE-g-MAH added, POE-g-MAH increases the contact between the glass fiber and Bonding force between resins and functions as an interfacial compatibilizer to compensate for the role of the coupling agent owing to the loss of the glass fiber’s surface during processing.
3. The mechanism seen from the rheological curve
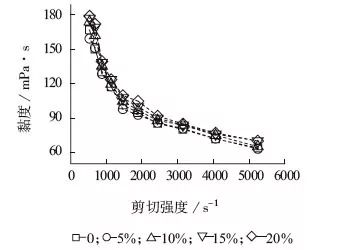
Rheological curves of PA6T/66 with different POE-g-MAH content
The shear effect of the screw on the melt can be effectively transmitted by increasing the viscosity of the system, which also improves the dispersion/distribution of glass fibers. This is one possible mechanism of action of the toughening agent POE-g-MAH in glass fiber reinforced high-temperature nylon materials. Since the viscosity difference of PA6T/66 with different POE-g-MAH content is not readily apparent, it is thought that the change in the melt viscosity of the system brought on by the toughening agent is not the primary cause of the material’s obvious improvement in its mechanical properties.
It was planned to add a 0.5 percent aminosilane coupling agent to the PA6T/66 and PA66 systems. The above table shows that while the mechanical properties of the glass fiber reinforced PA66 system are hardly affected by the coupling agent, they are significantly enhanced in the PA6T/66 system when the same amount of coupling agent is added. The experimental findings supported the hypothesis that the surface coupling agent for glass fiber will deteriorate and lose effectiveness at high processing temperatures and that the toughener will improve the interfacial compatibility of high temperature nylon resin and glass fiber.
Conclusion:The strengthening impact of POE-g-MAH in such systems results from the degrading loss of coupling agent on the surface of glass fiber caused by the higher processing temperature of high-temperature nylon. The coupling agent experiment findings supported the hypothesis that high processing temperatures would cause the glass fiber surface coupling agent to deteriorate and lose its effectiveness, and that the toughener would improve the interfacial compatibility between high temperature nylon resin and glass fiber.











